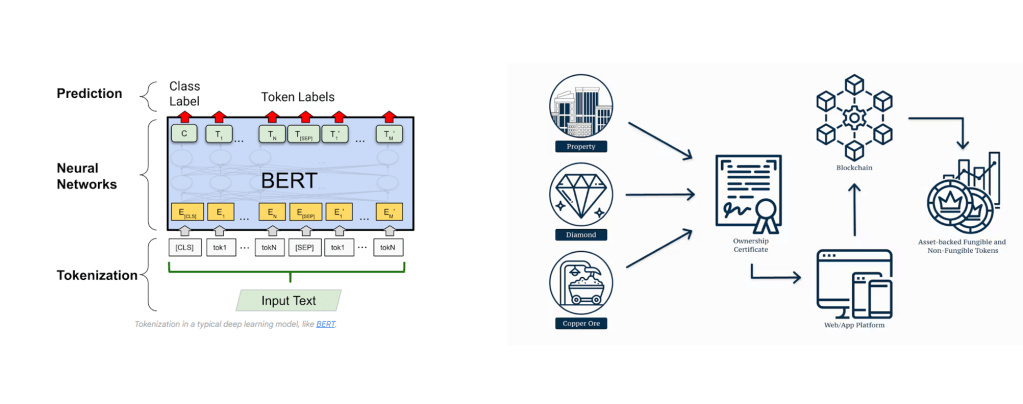
Tokenization in Cryptocurrency
Definition and Purpose: In the realm of cryptocurrencies, tokenization refers to the process of converting rights to an asset into a digital token on a blockchain. This approach can encompass a wide range of assets, from real estate and artwork to ownership stakes in a company.
Technology: Utilizes blockchain technology, a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring security and transparency.
Types of Tokens:
- Utility Tokens: Offer access to a future product or service.
- Security Tokens: Represent an investment in an asset, providing rights such as ownership, dividends, or interest.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Represent unique assets, allowing for the digital ownership of a one-of-a-kind item or piece of content.
Benefits:
- Liquidity: Tokenization can increase the liquidity of high-value assets, making them more accessible to a wider range of investors.
- Fractional Ownership: Enables investors to own a portion of an asset, lowering the barrier to entry.
- Transparency and Security: Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures that ownership and transactions are securely recorded and easily traceable.
Tokenization in Large Language Models (LLMs)
Definition and Purpose: In LLMs, tokenization refers to breaking down input text into manageable pieces, called tokens, that the model can understand. These tokens can be words, subwords, or characters, depending on the model’s design.
Technology: Utilizes natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to analyze, understand, and generate human language.
Types of Tokens:
- Word Tokens: Treats whole words as single units.
- Subword Tokens: Breaks down words into smaller units, capturing morphological variations.
- Character Tokens: Analyzes input at the character level, useful for languages with rich morphology or when dealing with unknown words.
Benefits:
- Flexibility in Handling Varied Input: Tokenization allows LLMs to process and understand a wide range of human language inputs.
- Efficiency: By breaking down text into tokens, LLMs can efficiently process large amounts of data, enabling rapid response generation.
- Improved Understanding: Subword and character tokenization can help models better handle unknown words, slang, or new vocabulary, improving the model’s accuracy and adaptability.
Comparison and Insights
- Foundation: Both utilize the concept of tokenization but on different technological foundations—blockchain for crypto and AI/NLP for LLMs.
- Purpose: In crypto, tokenization primarily aims to democratize access to assets and enhance liquidity. In LLMs, it serves to improve language understanding and processing efficiency.
- Impact: While crypto tokenization has the potential to revolutionize asset ownership and investment, LLM tokenization advances the capabilities of AI in understanding and generating human language.
- Challenges: Crypto tokenization faces regulatory, security, and market volatility challenges. LLM tokenization, on the other hand, deals with linguistic complexity, context understanding, and ethical concerns like bias and misinformation.
Concluding Thoughts
Tokenization, as a concept, showcases the transformative power of digital technologies, whether in democratizing asset ownership through cryptocurrencies or advancing language understanding in AI. Each application reflects a different aspect of tokenization’s versatility, highlighting both its technical intricacies and its broader implications for digital innovation and societal change. This comparison not only illustrates the multifaceted nature of tokenization but also underscores the ongoing evolution and impact of digital technologies across diverse domains.
Leave a comment